Social Layer Whitepaper v2.0
Contents
- definition and vision
- product
- users and use case
- comparison with related products and concepts
- technical solution and route
- product launch and growth
Definition and Vision
Definition of Social Layer
A subjective, relational and programmable Soulbound NFT-based social network.
Vision
Our vision is to empower and free individuals to identify, create, and enrich social networks centered on the concept of "individual".
The cornerstone of individual freedom is the right and ability to say "no" to existing options and systems. Today's trust networks or social relationships are dependent on various hierarchies and market system; these social evaluation systems rely on external materials and are far from humanity. People living within are prone to feel powerless because of the vagaries of externalities.
But when he wants to live beyond this, how can he build trustworthy human relationships, why should the unfamiliar world trust him? If he wants to experiment with new social structures outside the known ones, what tools should he use, with whom and with what references?
In the age of borderless organizations, empowering people to feel confident when leaping into unknown social environments is central to achieving personal liberation. The goal of Social Layer is to create new ways of human connection, allowing everyone to build diverse social roles and reputations, and experimenting pioneering social structures on top of a decentralized network of trust.
Social Layer builds a new layer of structures that intertwine with the spiritual, emotional, and subjective world of human beings, above the basic level of human society that satisfies basic survival. By recording information about multiple interpersonal relationships that are not determined by a single organization, it presents individuals with his or her own value coordinates, as opposed to the monetary and material ones. The organization will not constitute a boundary or shackle for individual development. Anyone can leave the organization or their existing relationships and create a new trust and organizations upon Social Layer.
Social Layer will create not only more freedom of choice, but also the courage to choose freely.
Product
Terms
badge
A collective term for all types of tokens issued in the Social Layer ecosystem. Badges come in many varieties, including but not limited to evaluation badges, role badges, contribution badges, and gift badges.
creator
The one and only one original creator of the badge.
issuer
The person who has the authority to issue the badge.The issuer can be either the creator himself or the person(s) authorized by the creator. creator has the right to grant and cancel issuance rights.
issuee
The first person to receive the badge, the same as the person to whom the badge is issued. There is one and only one.
badge owner
The issuee can choose to transfer the badge to anyone. The issuee's information is retained on the badge, but the badge owner enjoys the other benefits (if any) that the badge carries. Here Social Layer respects the holder's wish to gift the transfer while maintaining the token's soulbound information.
domain name
The unique identity domain that users have in the Social Layer ecosystem.
badge domain
All badges, in addition to their name, also have a unique badge domain name, and all badge domains are suffixed with the creator's identity domain name; the prefix is customized. Therefore, it is clear for each badge, no matter how it circulates, who initiated it.
badge template
To support multiple usage scenarios, users can combine and build customized badge templates using the badge components provided by Social Layer.
badge graph
Visualize the relationships connected by badges.
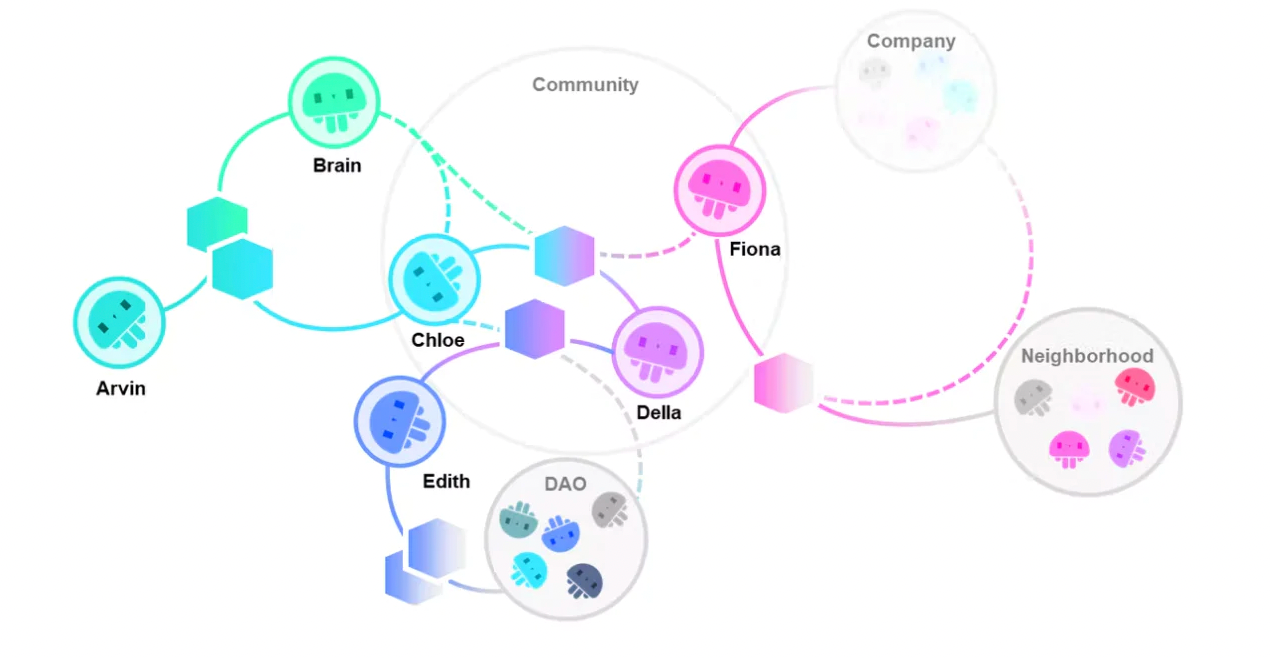
Function
Create a badge
The badge image, badge name and badge domain are the most basic information needed to create a new badge.
Issue
The most basic requirement for successful issuance is to record the reason for issuance. Any user can issue an issuee by filling in the wallet address or identity domain.
Accept
When you select Accept, the badge is minted on the chain and cannot be changed. If you select Reject, it will not be displayed in the user identity.
Use a Badge template
- Activity-based template, including an "Activity Participation" component and an "Evaluation" component, allow issuers to associate specific activities when evaluating a person.
- Role-based template, including a "Role" component and an "Evaluation" component, allow issuers to associate and evaluate related roles during evaluation.
- NFT-based template, including a “Custom NFT” component and an "Evaluation" component, allow the issuer to associate any NFT asset, such as a painting, a book, or a song, when giving an evaluation.
- Gift-based template, including an "Evaluation" component and a "Ticketing" component, allow the issuer to give a rating while granting the holder of this badge the right to redeem it. Subsequent use of the entitlement is reflected in the consumption of the "Ticketing " quantity.
- Badge aggregation template, which are programmable templates that allow users to trigger a new badge issuance once they have collected enough specific badges; the latter aggregates information from the former. This is useful for schools to set up "graduation" badge issuance based on course completion, or community "membership" badge issuance based on task completion.
Users can combine components at will to create badge templates suitable for their own scenarios.
Explore Relationships
By domain name or keyword, you can search for related badges and users. It is possible to browse badges that have been awarded and accepted by other users; it is also possible to browse the total number of recipients of the badge. (For privacy reasons, the search may be limited to second-degree contacts)
The badge graph also allows users to discover fresh relationships at a glance.
Replication of programmable social structure prototypes
When anyone tries to create a new social organization, he can browse and copy the social structure of other organizations in Social Layer. This structure includes, but is not limited to, core badge types, rules for obtaining badges, and rights that come with badges. As well, depending on new needs, these rules and rights can be reprogrammed, facilitating rapid iteration and experimentation with social organizations.
Social Layer-based dApp features
- The Career Development dApp based on badges can allow users to find potential employees with special skill badges, or social learning certifications, . For example, someone who has been awarded the "Tech Bigwigs" by a programmer, or someone who has the "Outstanding Graduate" badge from some web3 universities.
- The dating dApp based on badges can allow users to target people with badges like "Genuine Respect for Women" or "Seeking Equality and Non-Attachment". Of course, a programmer could also use the "Tech Bigwigs" badge to find a like-minded partner.
- A certification dApp plug-in that allows any non-diploma educational institution to set cascading, PBL course completion badges for students within their dApp and combine these badges into a final graduation certification.
Users and Use Cases
Application Scenarios
DAO and consensus communities
Two issues have arisen in the development of DAOs: the establishment of digital identities for members and the establishment of peer-to-peer relationships within the community.
In a decentralized community, members often take on more than one role. How is each role identified? How is it retrieved? How can it be verified as real? There is no simple Web3 solution to these problems. Currently, many community members' identities are limited to being presented with a nickname identifier in Discord, and a few cast NFTs for core members.
Social Layer is based on the Badge Aggregation Template, which creates a new way to record members' contributions and information about their roles. Completing specific tasks or collecting specific badges can be the basis for earning advanced status. Social Layer allows different badges to be combined into new badges, making members' identity information transparent and traceable.
Also, most ROLE-NFTs or POAPs are currently issued according to uniform rules from the community. A single rubric tends to overlook the value of unplanned, subjective, or emotional aspects. The vibe that makes a member feel excited and unique is often difficult to quantify or objectively assess. Therefore, Social Layer helps any member to keep track of the impact that others bring to the table. This will allow more connections to happen between members, not just between members and the community as it does now.
Social Layer can leverage the power of each member to weave a network of diverse values within the community.
More importantly, this network is not only able to be seen from within the community, but anyone who is connected to a community member is able to explore the relationships between people from the nodes they trust. As a result, the honors and evaluations anyone receives within a community are not closed off to the community either; he can easily show them to people outside the community; or even if he leaves the community, the relationships built up by these badges still exist.
Hackathon and Burning Man Festival
After an event, POAP can record the connection between the participants and the event organizers, and social media followers and fans can connect people who didn't know each other.
But what is the substance of this starry mesh of connections? A thinks B is the "Genius Illustrator" of the Web3 concept? B thinks C is the "Solidity Language Artist”? D Thinks E is the "Master of IRL Events"? --It is the badge that offers the opportunity to record these specific connections.
More importantly, when the next Hackathon or festival happens, those who have received badges will be searched by others. Looking for teaming partners? Search for the recipients of the "Solidity Language Artist" badg. Looking for camp setup partnerships? Search for the recipients of the "Master of IRL Events" badge!
Also, people who have been awarded the same badge by the same person at different events can find each other. If C trusts B's judgment, then when he is looking for an engineer, he can first explore the recipients who also have the same "Solidity Language Artist" badge.
Originally this decentralized evaluation information was non-existent for the event organizers, and for those outside the event; for the two parties connected by the badge, most of the time, there was no record of it.
Social Layer not only allows information that respects multiple values to be mapped on a decentralized network, but also allows these relationships to be retrieved and become nodes of trust transfer.
Social Learning
Social learning is not just a non-diploma based training that adults participate in after work; more and more middle and high school students are also PBL students participating in programs outside of school and becoming part of social activities.
These unofficially certified trainings and practices are playing an increasingly important role in the accumulation of human skills and experience. What results have been obtained from the training? What impact did the practice have on the team or others? What level of skill has been achieved? --These are both evidence that can be provided when seeking education and employment, and an important part of identity information in an increasingly mobile society.
In Social Layer, the creator, issuer, recipient and the badge itself all have a domain name that is unique to the entire domain. The relationship between the badge and the creator and issuer cannot be forged, and the relationship between the recipient and the badge cannot be forged. This will also significantly reduce the problem of third-party difficulties in verifying the authenticity of diplomas or learning records in social learning scenarios.
For providers of social learning, traceable and retrievable badges, which avoid forgery and fraud, help them maintain their reputation and build community that way.
Charity and Mutual Aid Organizations
There are very many volunteer activities and acts of mutual support in life that are difficult to record, display and search.
Disaster relief, long-term support, regular counseling services, etc., whether across cities or within communities of residence, all have positive externalities on society.
However, the market mechanism, in which money is the primary medium, does not record these values.Social Layer's badging tools can be used to capture them and constitute a truly meaningful and humanly cherished network of values.
Before Social Layer, adjectives like "unsung" were often used to praise people for their philanthropic endeavors. But we want their impact to be marked by the beneficiaries and become an indelible part of their social identity.
More people can see what they have given, and it will give them more prestige. Based on these records, some organizations can use the "gift" component of Social Layer to associate their giving with benefits or entitlements.
Keeping the value passed on in the network is also an incentive for those who give.
Social Layer's changes to the scenarios above
Building trust
Trust is at the heart of social capital. Building trust online is more difficult than building trusting relationships offline, but mutual trust within a DAO is critical to improving cohesion within the organization. Social Layer builds the infrastructure for trust to transfer within and across communities.
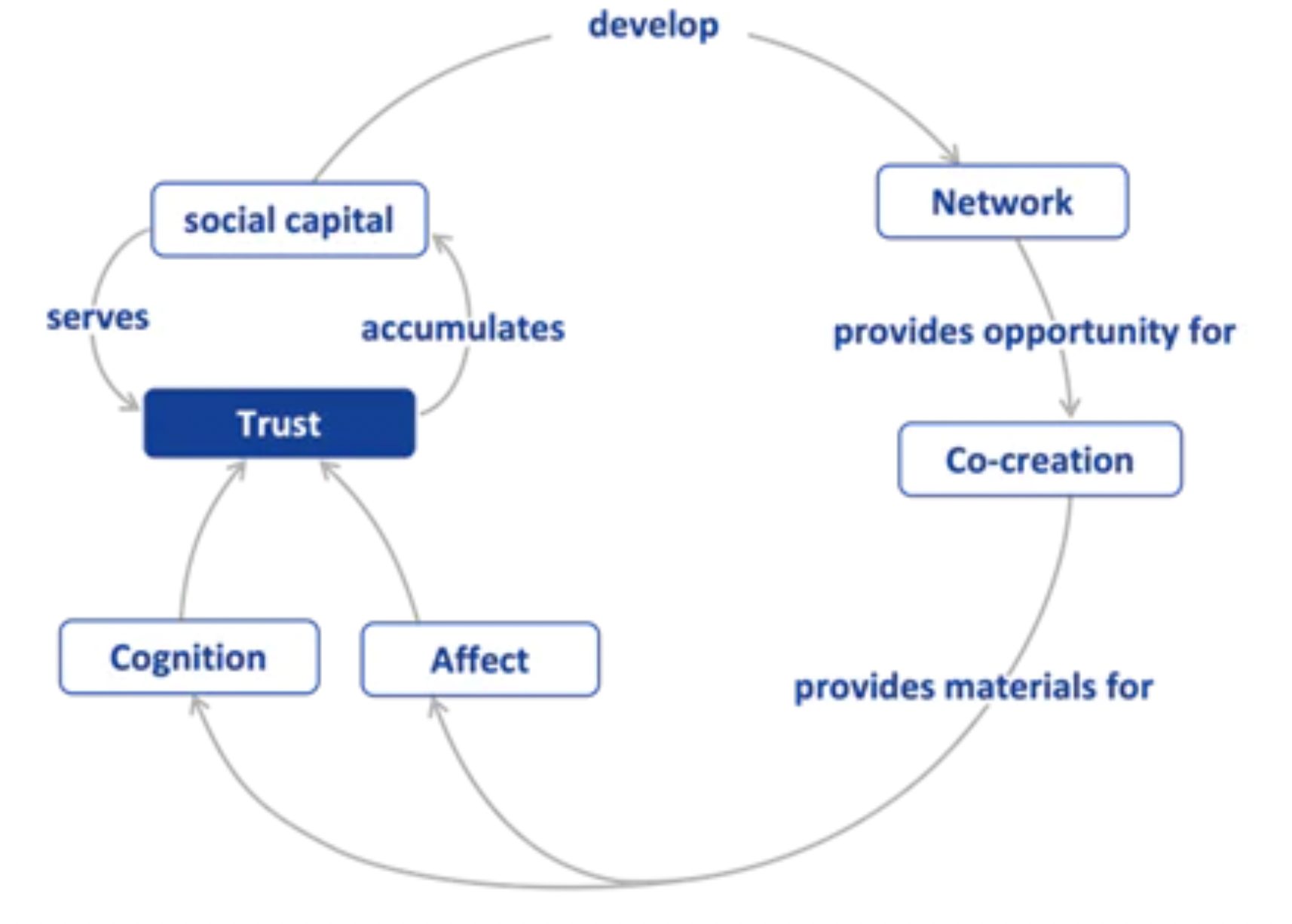
Sustaining and facilitating participatory community relations is not achieved through strict market-based contractual norms or hierarchical organizational power constraints, but rather through the construction of a reciprocal, subjectively preferred, mutually supportive interpersonal network. The structure and content of this network is the source of social capital.
If group members share a specific, informal set of values or norms, they can cooperate with each other.If group members expect others to behave reliably and honestly, then they will trust each other. social Layer provides communities and organizations with the very foundation of trust for such weak relationships.
Trust is not required if total information about another person is already known; trust cannot arise if total ignorance of another person's information is not known at all. This suggests that the amount of necessary knowledge required for trust lies between total knowledge and total ignorance, and that trust judged on the basis of information is conditional. Partial information is an important basis for assessing a person's trustworthiness, but it is also not the only basis for a high-quality trust relationship.
In order to reach mutual trust, in addition to cognition-based information, the affection-based information from a shared identity is even more crucial. social Layer not only records users' behavior and ratings, but also allows people with the same badge to discover each other. This satisfies both pre-requisites for high-quality transfer of trust.
The decentralized value network only provides fact-based information of the trustee without interfering with the trustor's judgment. The same badge has different degrees of trustworthiness in the eyes of different people. We give the power of judgment to everyone in the network, and untrustworthy badges will gradually lose importance, while trustworthy badges will emerge in a natural way.
Social Layer will spawn more relational commons in community scenarios: bringing people with common ideas together on a specific commons to freely discuss, act, collaborate, and communicate. The formation of each commons needs to satisfy 1) the actors' desire to establish or be established more interpersonal weak ties; 2) the actors' desire to obtain information to adjust their understanding and trust of others; 3) the actors' desire to find collaborative partners
Social Layer meets these needs, helping each community generate more chains of trust and prosper in more actions.
Building multiple identities and giving freedom of mobility
The badge system built around each individual by Social Layer helps him to have a diversified perception of his social role. Each badge records the power relationship with different people at different stages of life, different duties and missions, and, to some extent, different meanings.
His identity will be judged by others beyond his relationships with superiors and subordinates, his position in the bureaucracy, or his relationships with a limited number of people around him. His interactions with anyone, in any form, may become part of his identity. What he can do, what he is good at, and what kind of collaborative spirit he has are all information that can be presented in Social Layer.
Each badge can be searched as a connecting node, which creates the possibility for each person to be seen outside of the original organization or power structure. People who share common values are also more likely to be connected by badges, which also facilitates the creation of communities that are not bound by interests, but by values.
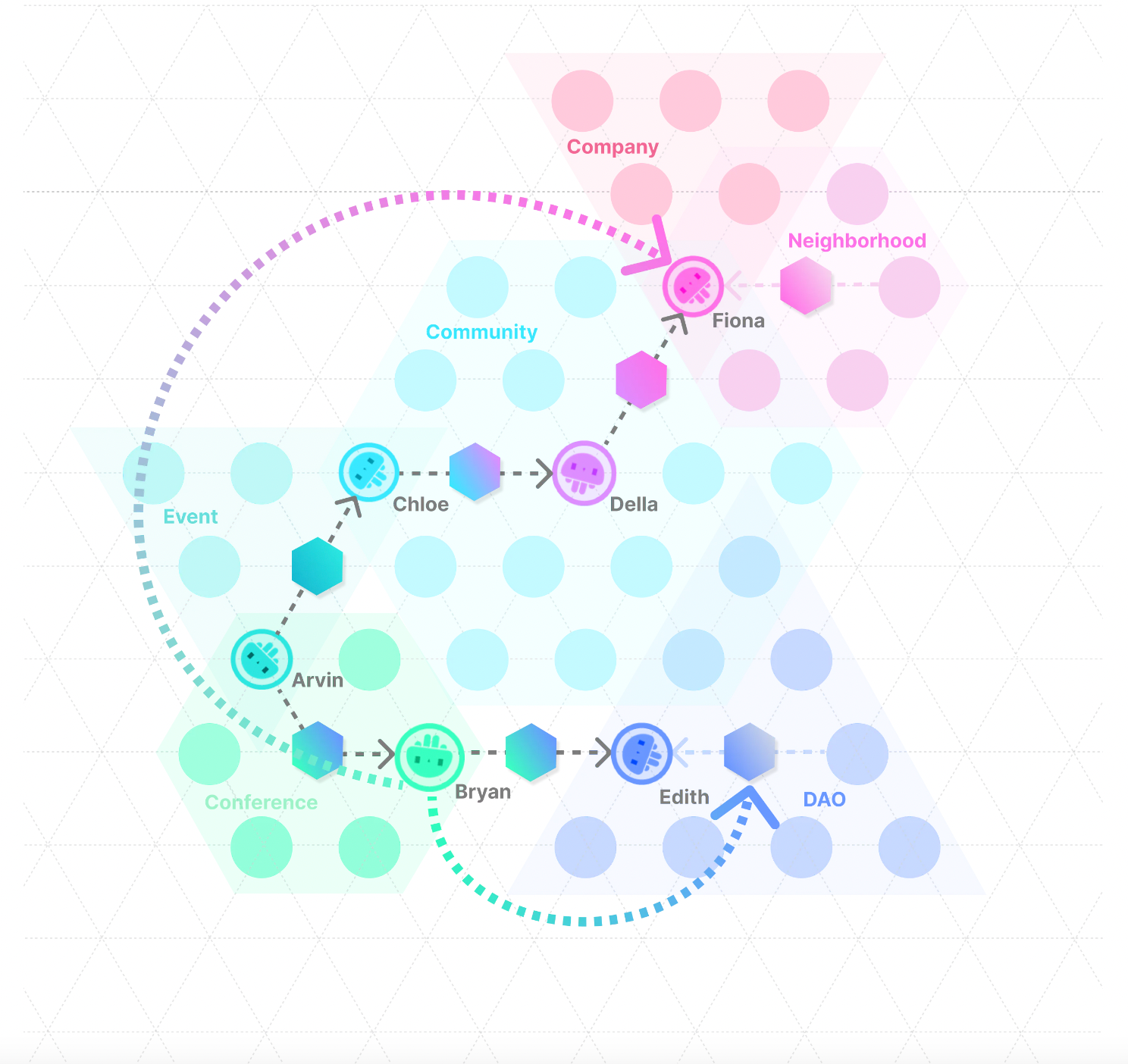
Visualizing and replicating programmable social structures
Social structure has long been an abstract concept that involves elements such as power checks and balances, cultural states, membership attributes and relationships within a community or organization. Few people have a clear view of what the social structure in which they live looks like. The pyramidal, hierarchical structure may be transparent to those at the top, but the vast majority of people do not have the opportunity or the right to peer into the full or detailed structure, and the imagination of what lies beyond the mainstream social structure is blank and tepid. But Social Layer is able to paint a clear picture of the structure of an organization or community through badges.
Especially for the consensus communities in the experiment, the most dominant subjective values emerging from a community, or how such values are constructed by rules, and how rights are formed, will be transparently visible.
More importantly, this badge-based NFT social structure prototype can be easily replicated and programmed to meet the needs of people who want to escape the mainstream social structure and experiment with alternative communities. What he and his co-builders got was not only a "community creation manual", but also an actionable and executable Layer of Society.
Comparison with Related Products and Concepts
vs related concepts
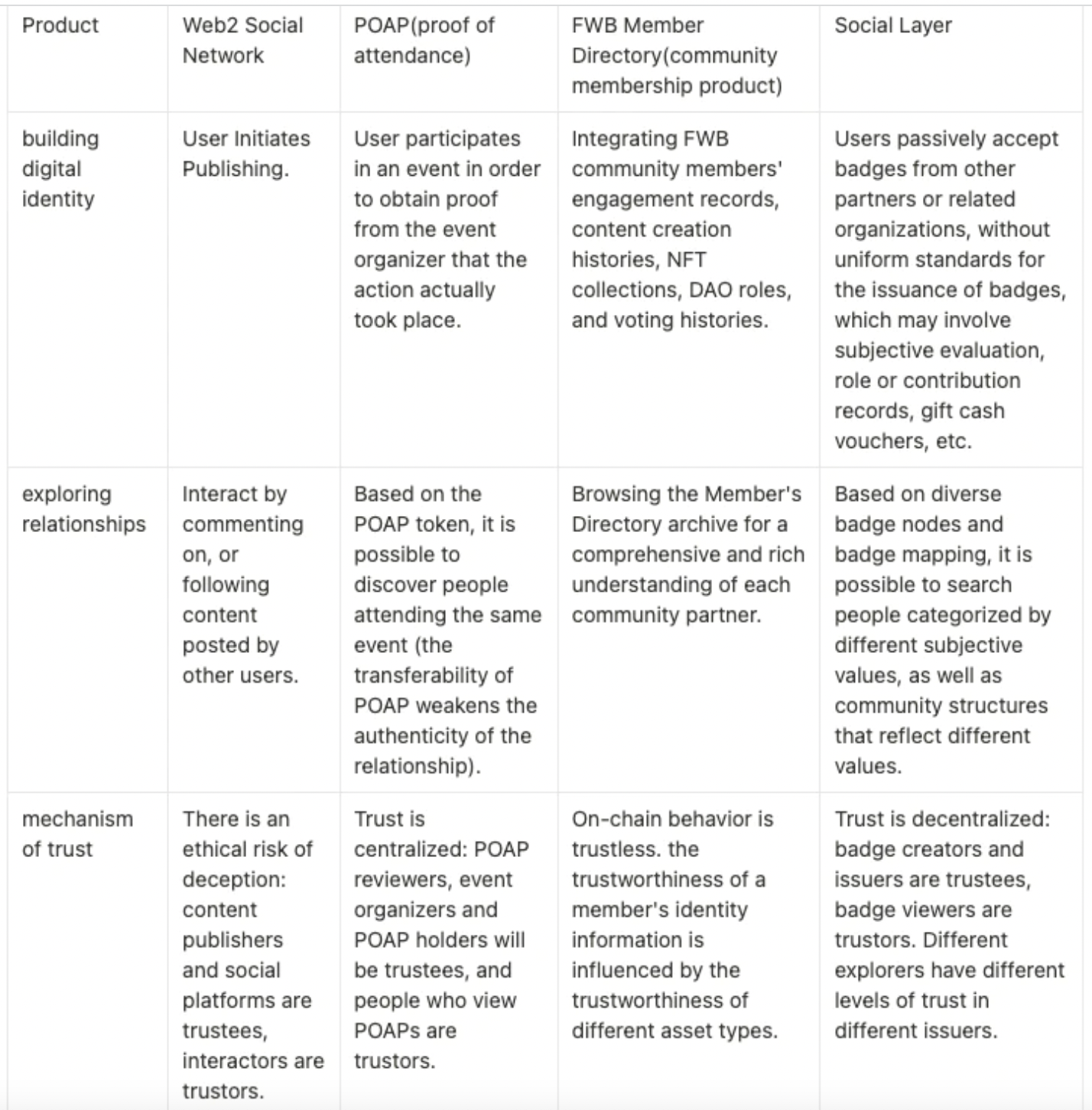
Social networks made up of badges are a new way of building social relationships that is different from the other two types of connections we are more familiar with in Web2 social media.
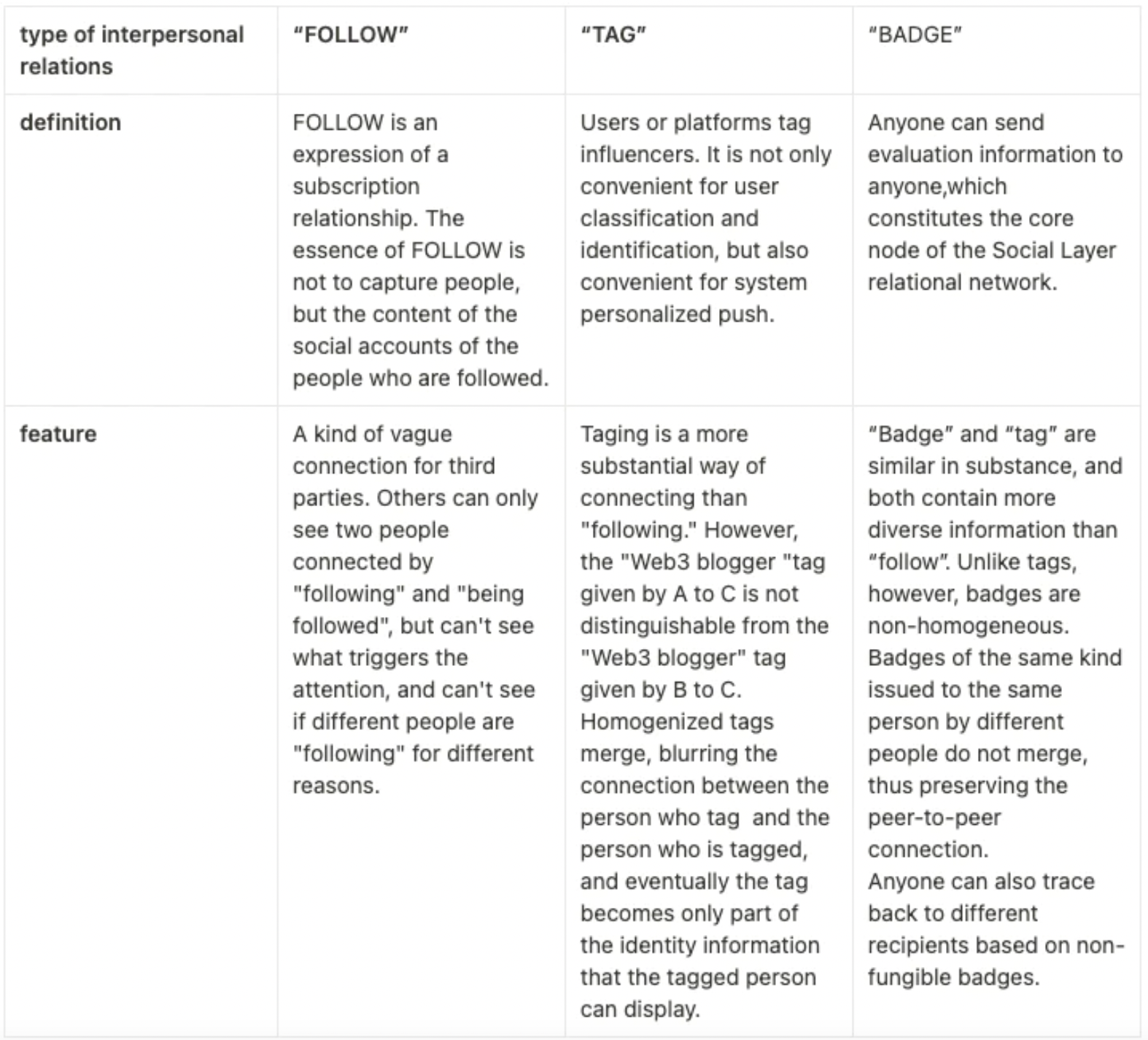
vs related products
Social Layer is different from other Web2 and Web3 products in three aspects: "building digital identity", "exploring relationships" and "mechanism of trust". In the comparison, you can see that the trust network built by Social Layer is different from the previous ones.
Technical Solution and Route
Solution
When users use Social Layer, they need to first create their on-chain identity, which is equivalent to a Profile Token, as a basis for participating in this network. Users will register their user names in the NameRegistry, and we use a mechanism similar to ENS/PNS, where the user's identity ID is a hash of the user's domain name based on the EIP-137 Namehash method to ensure that the data on the chain is streamlined and globally unique.
Social Layer has some information that needs to be stored under the chain, user profile details, pictures, badge description information storage, we will use Fleek's IPFS node.
To allow users to use Social Layer without worrying about gas overhead, we provide gas subsidies for identity creation, domain registration, and Badge casting, based on our GLMR pool. Our contract design includes a meta transaction mechanism, where a third party sends a transaction on behalf of the user, thus eliminating the user's gas. to prevent users from abusing the gas subsidy mechanism. We will limit the amount of gas per account per month, such as 200 per person per month. In the future, we can accept donations from users, apply for gas subsidies from Moonbeam Foundation, or let high-frequency users pay for gas themselves.
Social Layer badge is currently designed based on the ERC721 mechanism and meets the NFT interface standard.
Route
Social Layer will first be deployed on the Moonbeam network, the most mature Ethernet-compatible chain in Polkadot, with a flexible architecture, mature ecology and low transaction costs.
In the first period, we provide 10,000GLMR subsidy, which is enough to issue 500K to 1000K badges.
Later, we can build our own managed PoA parallel chain, but how to make it secure, reliable and decentralized requires further design and inviting community members to participate in maintenance.
Social Layer can run on different chains compatible with Ethernet, and in the future it will support multi-chain architecture to deploy in different ecologies. Arbitrum, ZKSync, Avalanche, Polygon, Godwoken are all platforms considered.
Product Launch and Growth
Launch
Social Layer will first work with the community scenarios mentioned in the sections above, such as DAO, which is building a membership system, the Web3 Industry Summit, innovative educational institutions that are blurring the boundaries of schools, and the Web3 social innovation and philanthropy platform.
We will initially take an aggressive offline approach to the rollout. Since concepts such as "badges" and "badge-built digital identities" are new, face-to-face education, demonstration and application in community gatherings is an important way to accurately communicate the Social Layer concept and values.
We plan to help participants hand-cast badges, distribute badges, and receive badges at offline events; and, as the event progresses, the mapping of relationships built from badges is mapped in real time on a large screen to visually help community members see relationships that would otherwise be invisible.
Growth
Using Social Layer to send and receive badges is only the first step in enriching digital identities. Further leveraging badges to link users is the key to unlocking the value of the protocol.
We plan to design a series of "find people" campaign, the theme can be "find cute men", "find atmosphere group players", " find the Brainiac", etc. In the campaign, we will develop a variety of badge filters and show users how to use badges to discover the treasures of second-degree connections.
We also plan to work with social and job search dApps to open up APIs and help them improve the accuracy of user matching with badge-based data.
The badge components and template designs will also be open to the Social Layer community. Users will have more freedom to decide what and how they want to award badges based on their needs.
Working with more public chains, users with different domains in different ecosystems can create badges directly in Social Layer with their domain name as the suffix.
Core contributors to the white paper:Eggy、Yibo、Jiang、Ren、Larri、Mango
Telegram:larri_supertramp;Twitter: layer_social
demo app: app.sociallayer.im
